HAIR & NAIL
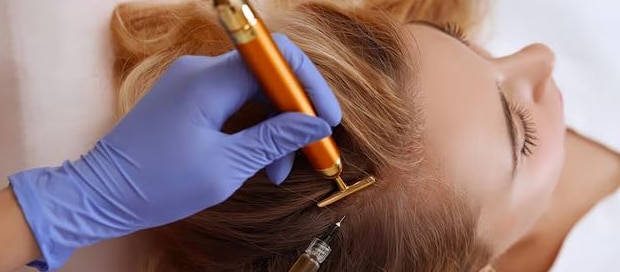
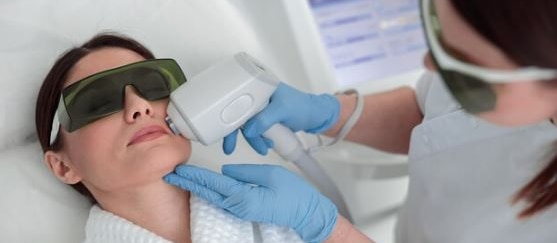
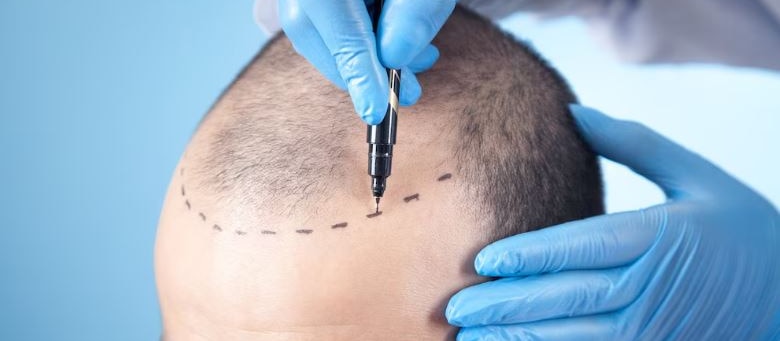
1. Hair Loss (Alopecia)Hair loss refers to the shedding of hair from the scalp or other parts of the body. There are different types of hair loss:Androgenetic alopecia (Male and Female Pattern Baldness)Alopecia areata (autoimmune-related)Telogen effluvium (temporary shedding due to stress, illness, or hormonal changes)Traction alopecia (hair loss due to tight hairstyles)Causes of hair loss include genetics, hormones, medications, stress, diet, and underlying health conditions.2. Hair TransplantA hair transplant is a surgical procedure in which hair follicles are moved from one part of the scalp (typically the back or sides, where hair is more resistant to balding) to areas with thinning or no hair. There are two main types:FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): Individual hair follicles are extracted and transplanted.FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): A strip of scalp is removed and then divided into follicular units for transplantation.It's considered a permanent solution, although the transplanted hair will still follow the natural hair growth cycle.3. PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma)PRP therapy is a non-surgical treatment where a person's own blood is drawn, processed to concentrate the platelets, and then injected into the scalp. The growth factors in the platelets are thought to stimulate hair follicles, promoting hair growth. PRP is used for:Early stages of hair thinning or androgenetic alopecia.Alopecia areata and other forms of hair loss.It's typically used in conjunction with other treatments or as a standalone therapy.4. GFC (Growth Factor Concentrate)Similar to PRP, GFC uses growth factors extracted from the patient’s own blood to promote hair growth. However, GFC usually involves a more advanced technique to further concentrate the growth factors and may be more effective in some cases. The procedure involves injecting these growth factors into areas of hair thinning or loss to rejuvenate hair follicles.5. Alopecia AreataAlopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks hair follicles, leading to round patches of hair loss on the scalp or other body parts. It can be temporary or permanent and varies in severity. Treatments include:Corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and promote hair regrowth.Topical treatments like minoxidil.Oral medications to modulate the immune response, such as JAK inhibitors.6. DandruffDandruff is a common scalp condition characterized by the shedding of dead skin cells, often accompanied by itching. It can be caused by:Seborrheic dermatitis (a more severe form of dandruff).Dry skin or lack of moisture.Fungal infection (Malassezia).Sensitivity to hair products.Treatment often involves using medicated shampoos containing ingredients like:Zinc pyrithioneKetoconazoleSalicylic acidTar-based shampoosTreatment OptionsFor hair loss and alopecia, treatments range from topical minoxidil, oral medications like finasteride, to advanced procedures like hair transplants or PRP/GFC therapy.Dandruff can usually be managed with the right shampoo or by addressing underlying conditions like seborrheic dermatitis.Fungal Nail Infections (Onychomycosis)Diagnosis: A dermatologist may take a sample from the affected nail (nail scraping or biopsy) to confirm the presence of a fungal infection.2. Psoriasis of the Nails3. Nail Fungus (Tinea Unguium)Diagnosis: A fungal culture or microscopic examination is often done to identify the specific type of fungus.4. Nail Trauma or InjuryDiagnosis: The dermatologist will assess the extent of the injury, including the nail bed and surrounding tissue.5. Ingrown Toenails (Onychocryptosis)6. Nail Lichen Planus7. Nail Melanoma8. Bacterial Infections9. General Nail Care Advice10. Cosmetic Nail Issues
READ MORE